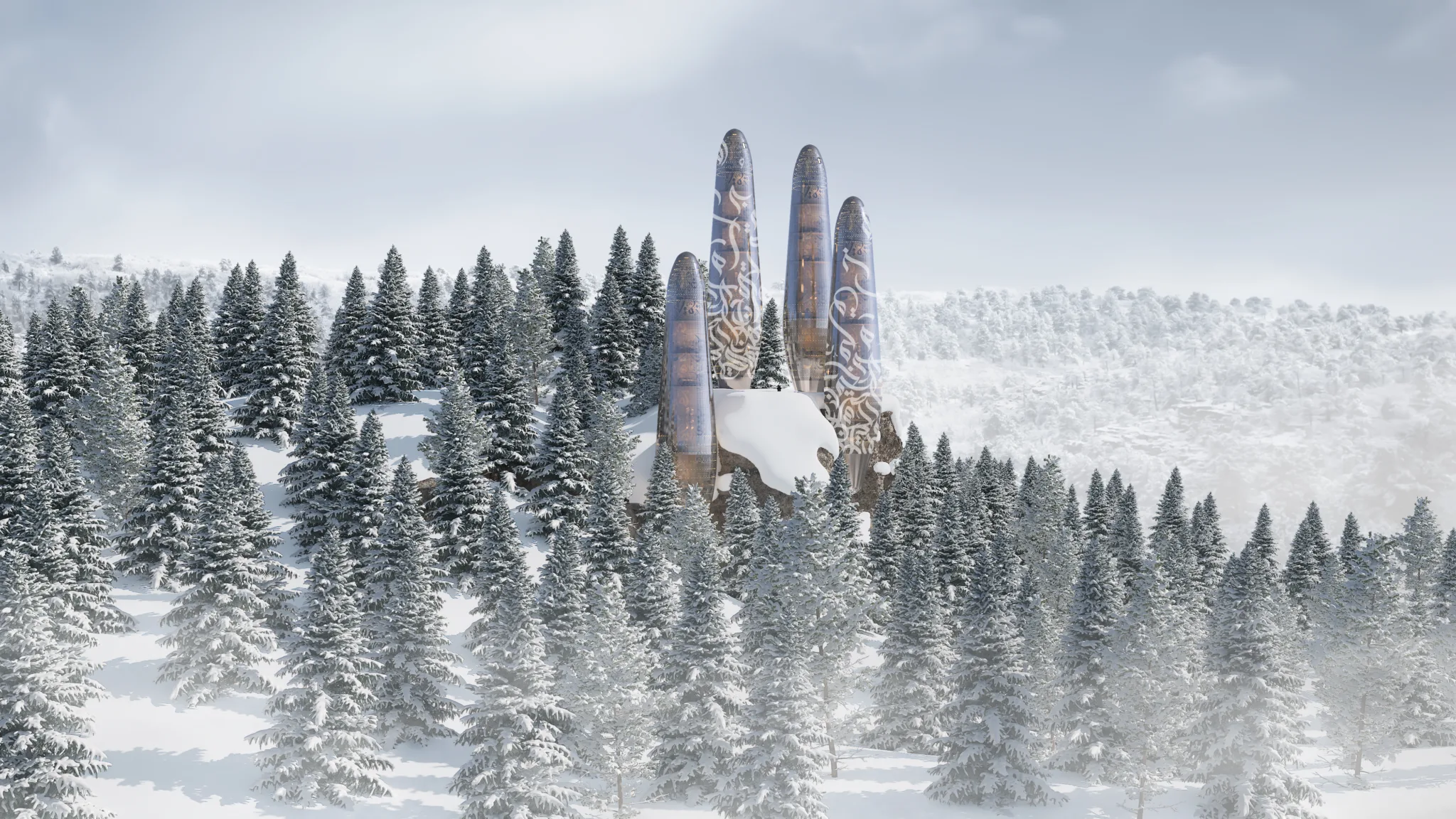
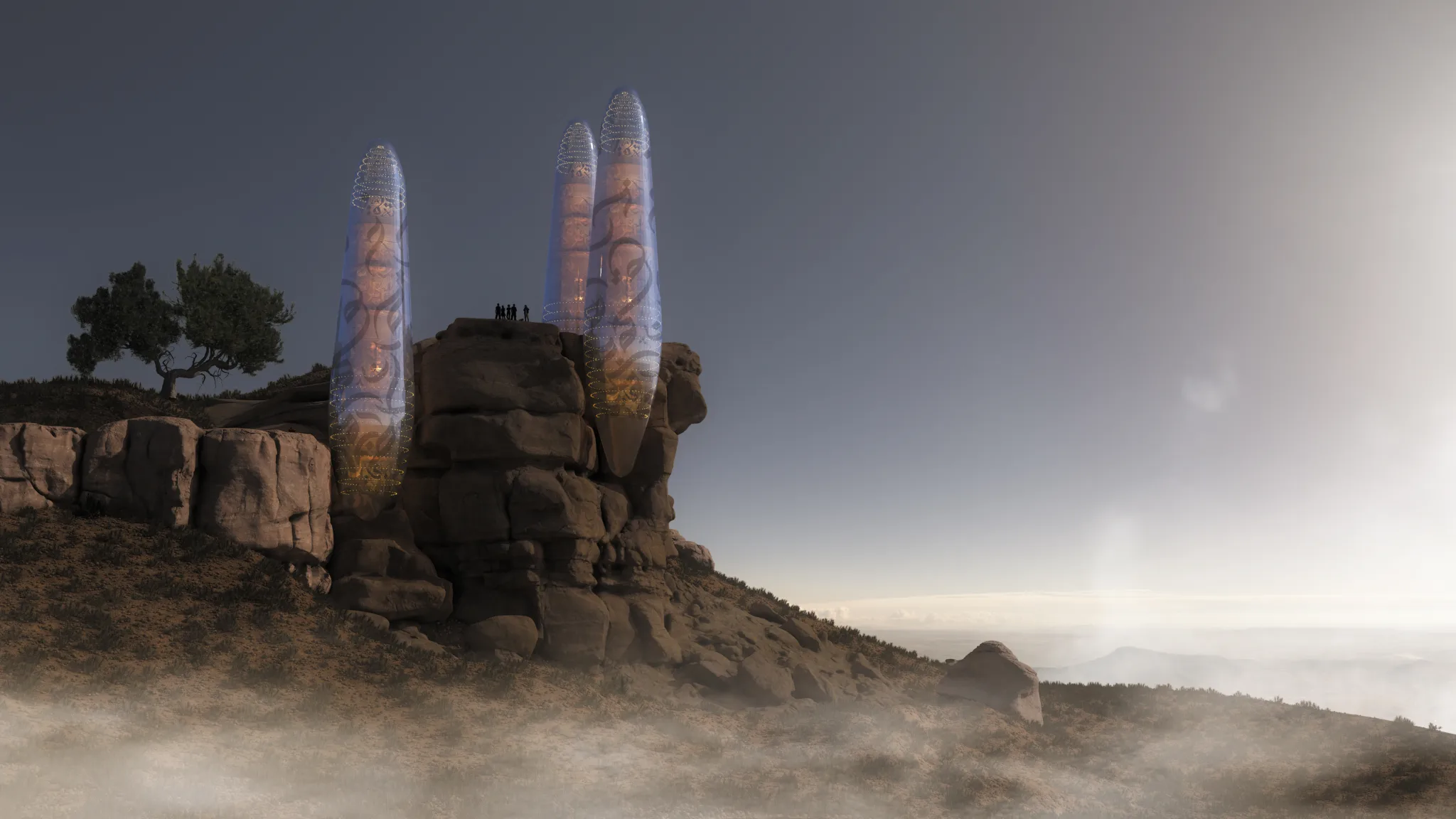
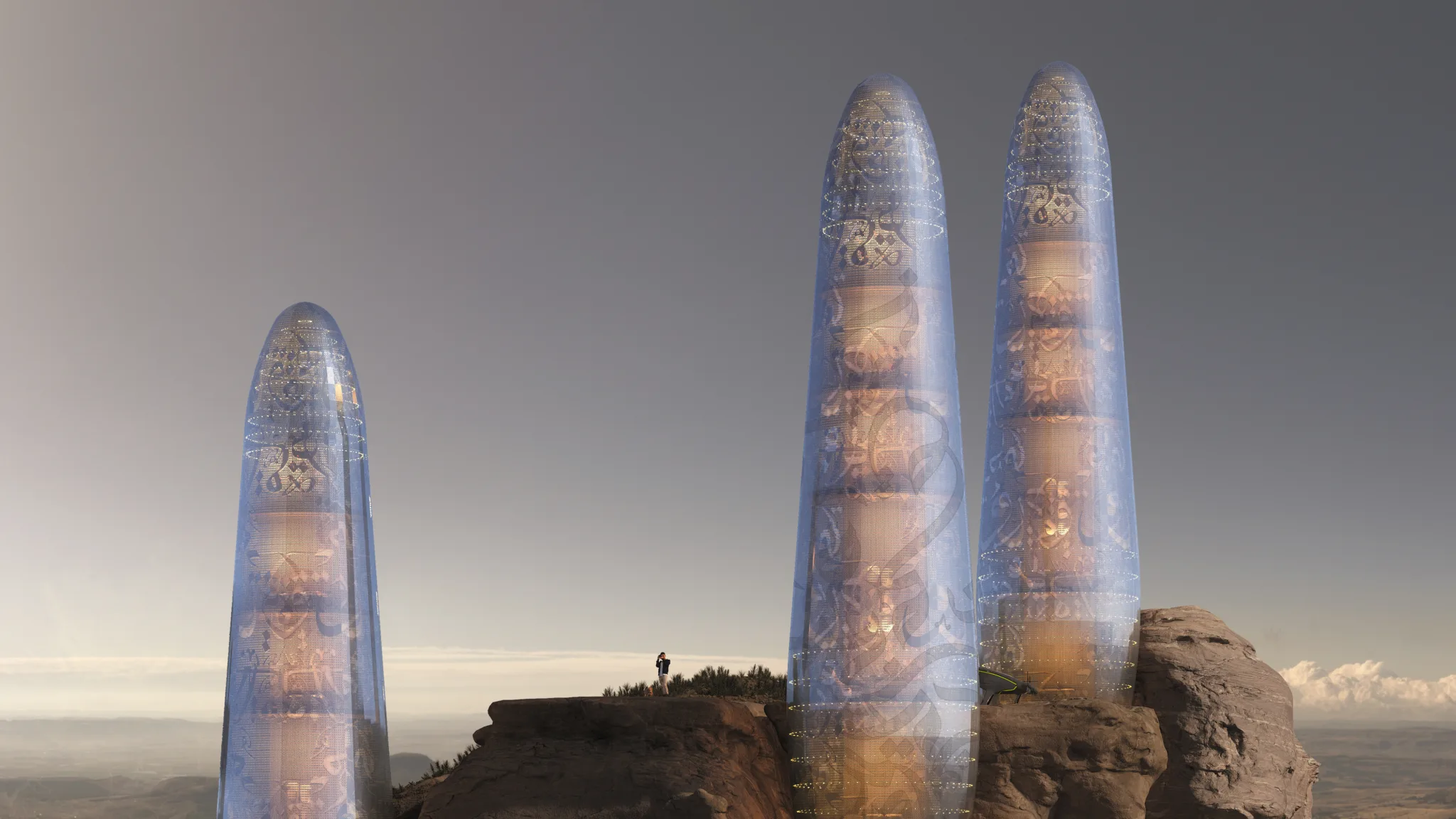
In the aftermath of climate disturbances and wars that have ravaged the planet's ecosystems, the necessity for innovative and sustainable living solutions has become paramount. The Asylum project presents a futuristic vision of single-family residential units designed to thrive in such adverse conditions. This scientific article explores the conceptual framework, design features, and technological advancements integrated into The Asylum, emphasizing sustainability, energy efficiency, and self-sufficiency.
The Asylum: A Visionary Approach to Post-Catastrophic Sustainable Living
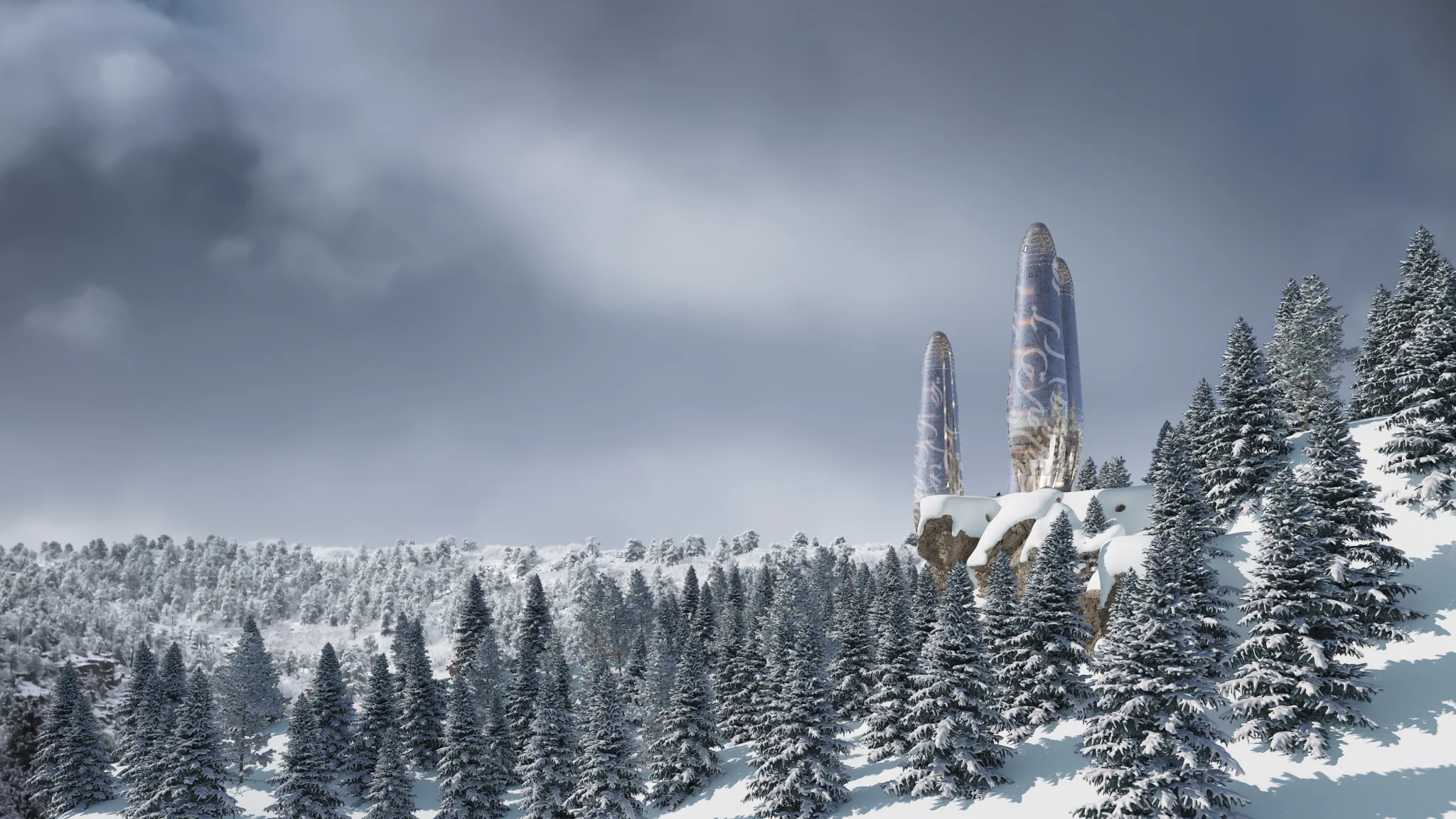
Humanity’s relentless exploitation of natural resources and persistent conflicts have precipitated a global crisis, culminating in the widespread destruction of ecosystems and rendering many traditional living environments untenable. The Asylum project emerges as a forward-thinking response, offering a blueprint for sustainable shelters capable of withstanding the harsh realities of a post-catastrophic world. This project prioritizes currently unavailable yet anticipated technological solutions, aiming to provide practical and resilient living conditions for single-family units.
Architectural Design and Layout
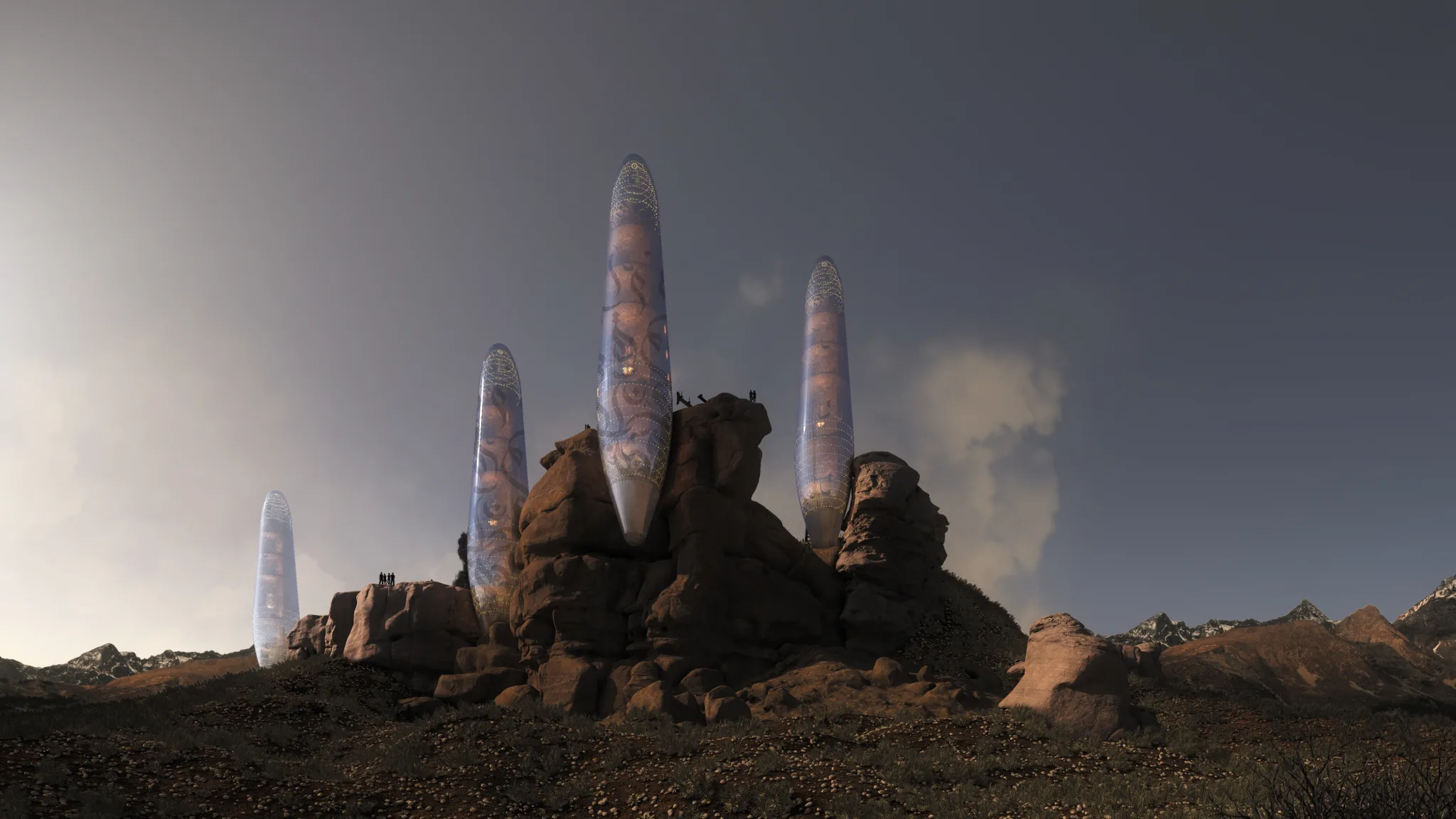
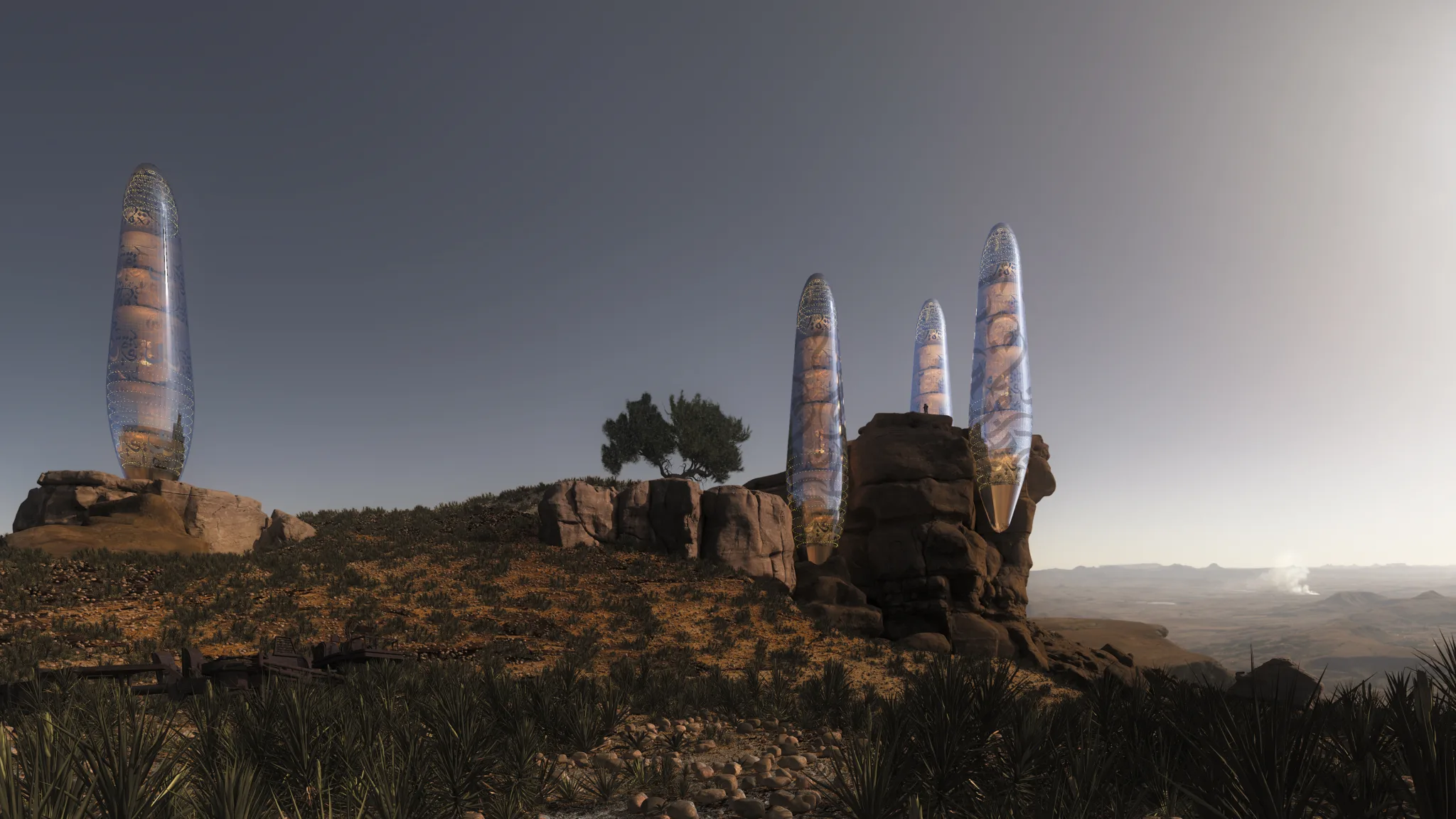
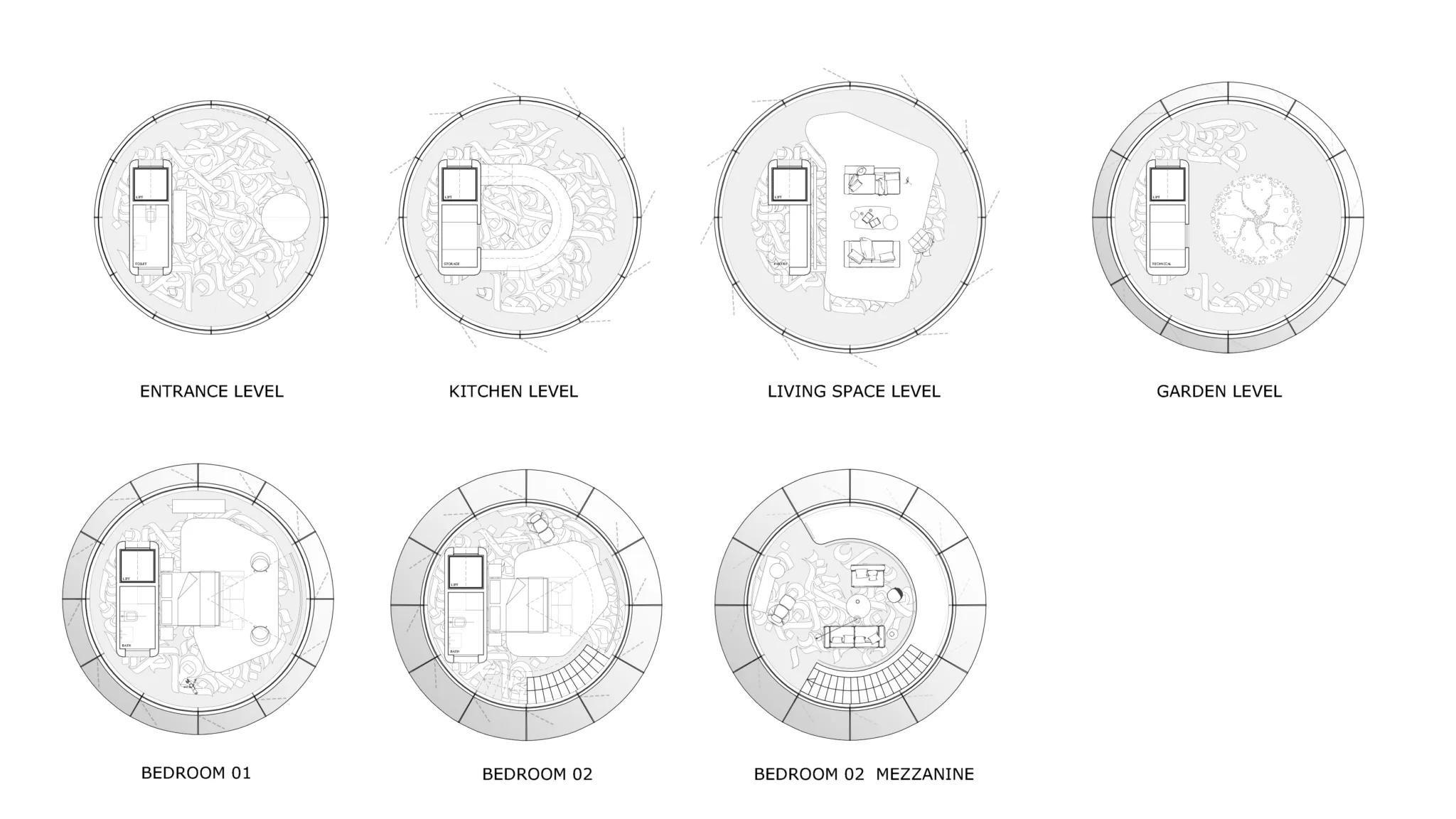
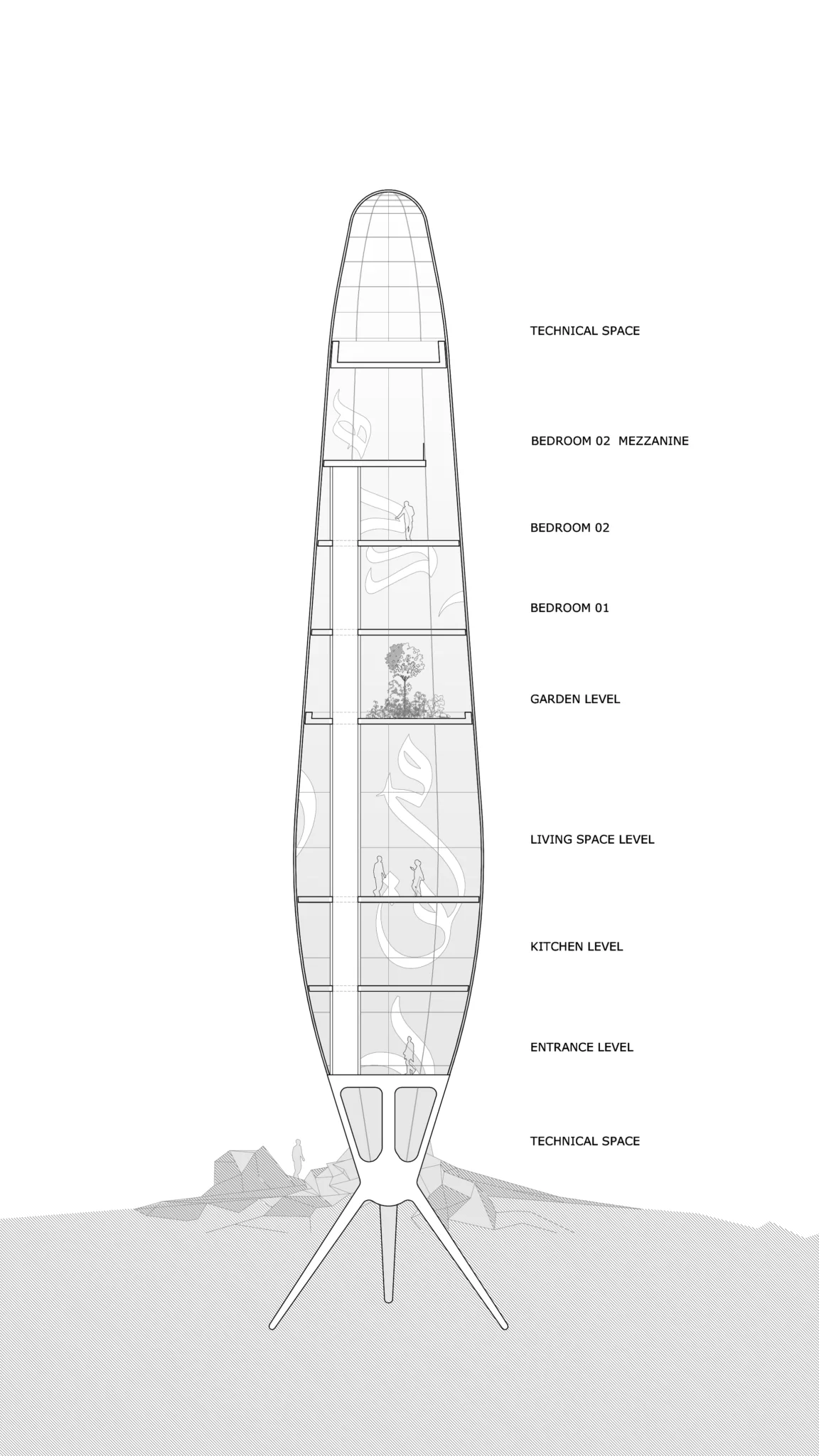
The Asylum is a single-family residential unit designed to accommodate a small family in a compact yet functional space. The unit comprises two bedrooms, a living room, a kitchen, and essential services. The architecture emphasizes simplicity, durability, and resource efficiency, ensuring the unit’s adaptability to various environmental challenges.
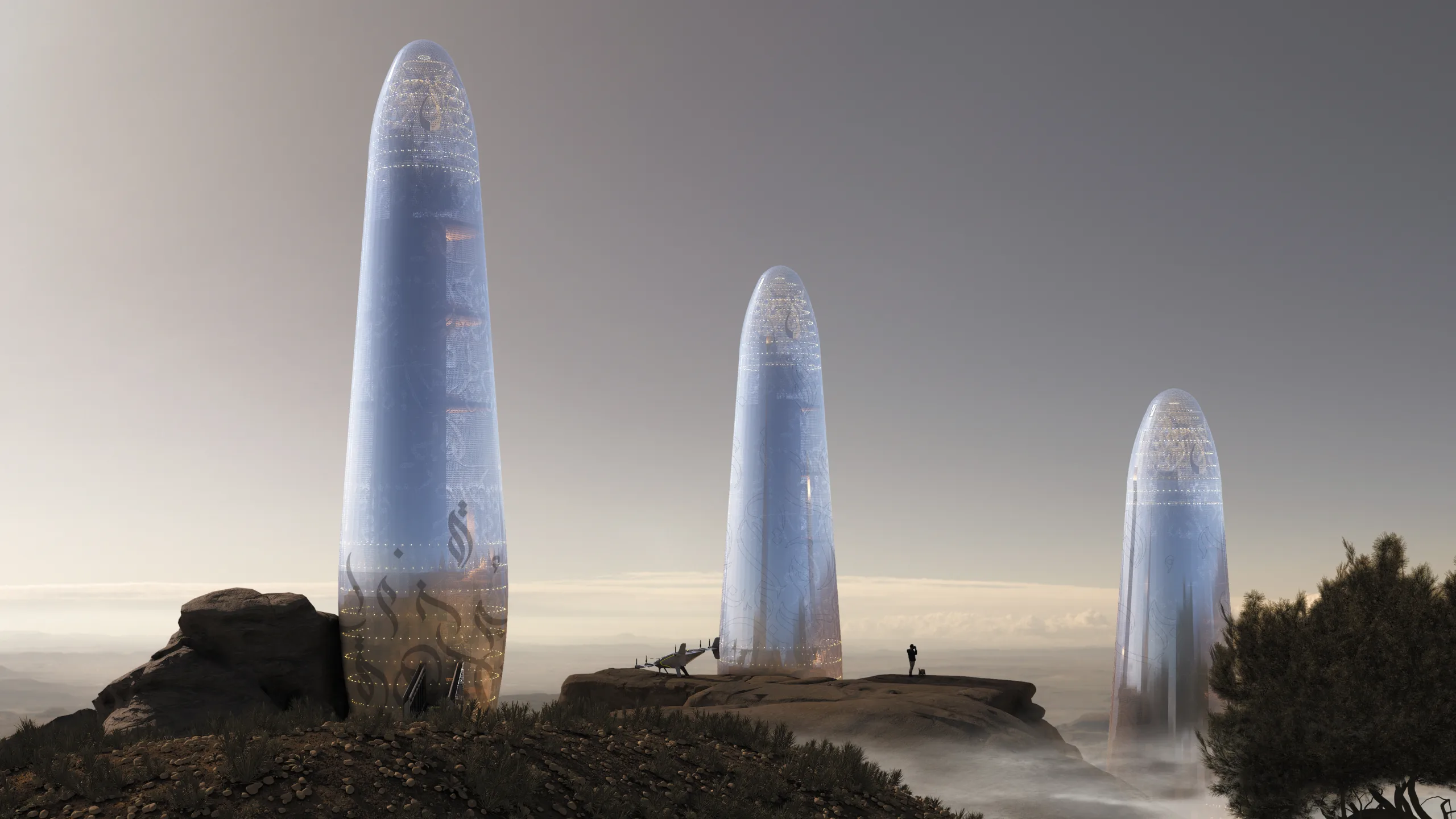
Smart Glass Outer Cover
The outer cover of The Asylum is constructed of smart glass, a material capable of converting sunlight and ultraviolet rays into electrical current. This innovative glass serves a dual purpose: providing natural light and generating renewable energy. The smart glass is embedded with Arabic calligraphy inscriptions, which not only enhance aesthetic appeal but also serve a functional role in energy conversion.
Rainwater Harvesting and Purification
A layer of advanced fibers integrated into the smart glass is designed to efficiently collect rainwater. This harvested water is stored in a tank located at the bottom of the building. To ensure potable water supply, the collected rainwater undergoes purification through exposure to ultraviolet rays captured by the smart glass. This method leverages the dual functionality of the glass, contributing to the unit’s self-sufficiency in water resources.
Motion Sensors for Energy Conversion
The floors of The Asylum are embedded with motion sensors that harness the kinetic energy generated by residents’ movements. This energy conversion system complements the electricity produced by the smart glass, ensuring a continuous and reliable power supply. By capitalizing on daily activities, The Asylum minimizes dependence on external energy sources, promoting a sustainable and resilient living environment.
Food Security through Agricultural Integration
Each residential unit within The Asylum includes a dedicated agricultural garden. This garden is designed to provide a portion of the residents’ food supply, reducing reliance on external food sources. The integration of urban agriculture not only enhances food security but also promotes mental well-being and a connection to nature in a post-catastrophic setting.
Wastewater is meticulously treated through advanced filtration and purification systems. Reclaimed water is then reused for irrigation in the residential garden and for non-potable purposes, significantly reducing water waste and promoting a closed-loop water management system essential for sustainable living in a post-catastrophic world.
The Asylum represents a pioneering vision for sustainable living in a world set by ecological and social upheavals. By integrating future anticipated technologies with innovative design principles, The Asylum offers a viable solution for resilient and self-sufficient residential units. This project underscores the importance of foresight in architectural and technological advancements, paving the way for sustainable habitation in an uncertain future.
Future Directions
Further research and development are necessary to bring the envisioned technologies of The Asylum to fruition. Collaborative efforts between scientists, engineers, and architects will be essential in refining these concepts and translating them into practical applications.