Parasite architecture is an adaptable, transient, and exploitative form of architecture that forms relationships with host buildings to complete itself. Parasitic structures are designed to use excess resources from the host building, such as energy, water, and space, to sustain their own existence. Parasite architecture is a response to the changing needs of urban spaces and the growing demand for sustainable and affordable housing. It is also seen as a way to repurpose underutilized or abandoned buildings, making more efficient use of existing resources. Despite its controversial nature, parasite architecture has become an increasingly popular trend in contemporary architecture and urban design.
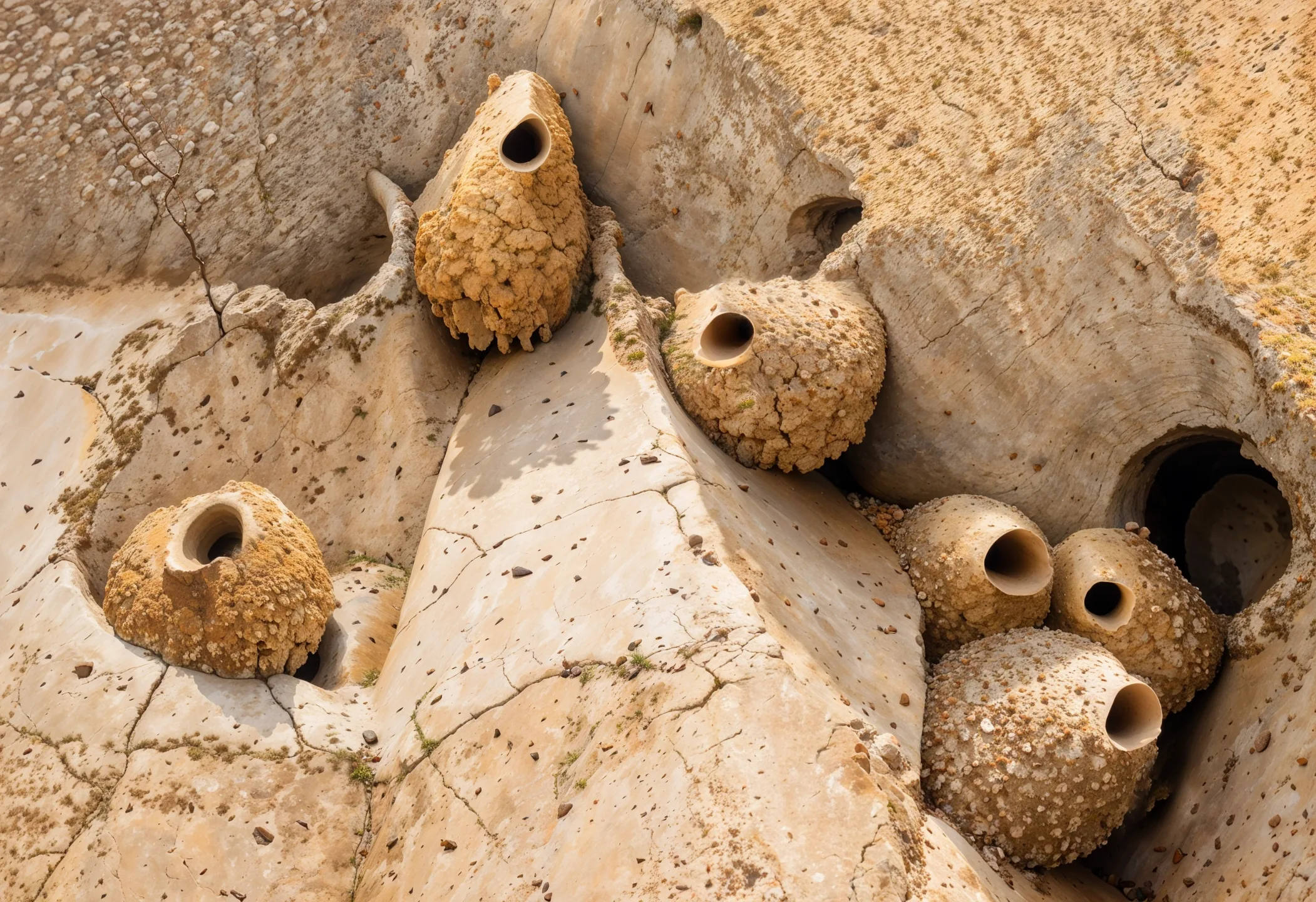
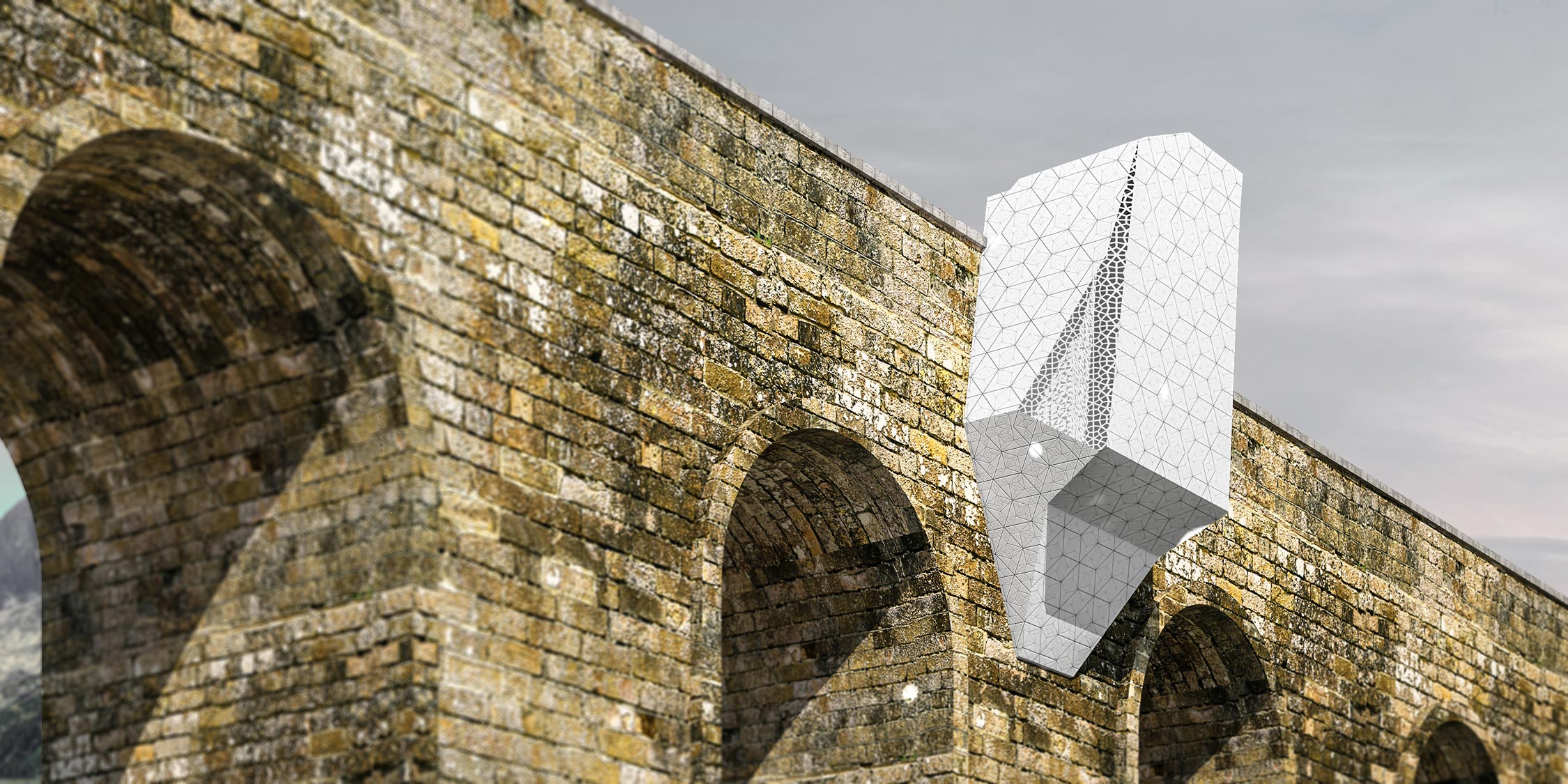
The Swallow Nest is a housing unit specifically designed for adventurers and campers that meets all their essential requirements. Its inspiration is drawn from the way a migrant swallow constructs its nest on various structures such as rooftops, light poles, cliffs, and even abandoned buildings. This dwelling falls under the category of parasite architecture, which is a versatile, fleeting, and exploitative form of architecture that must form associations with host buildings to complete itself. Parasitic structures cannot sustain themselves without drawing energy from the excess resources available in the host building.
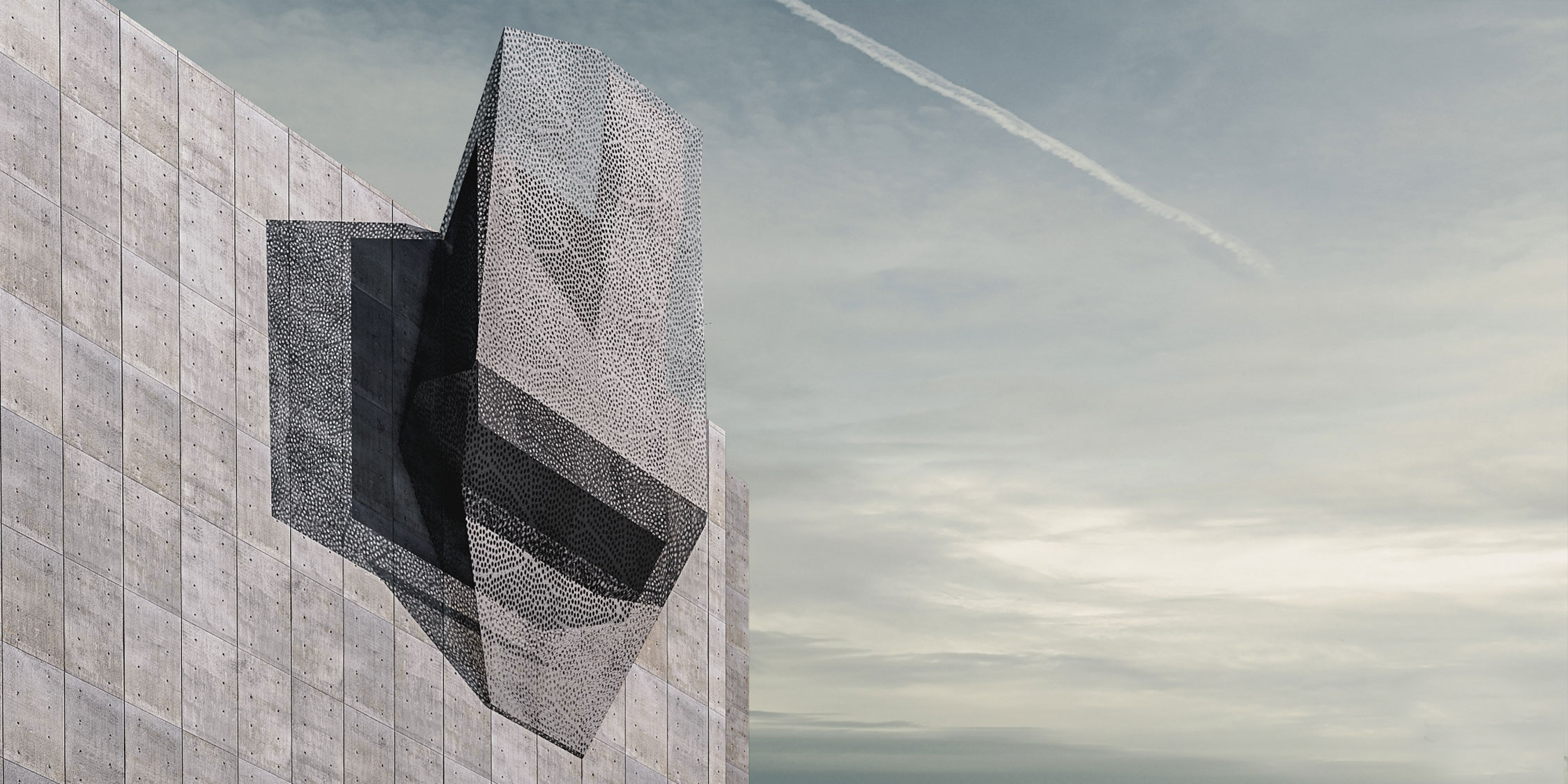
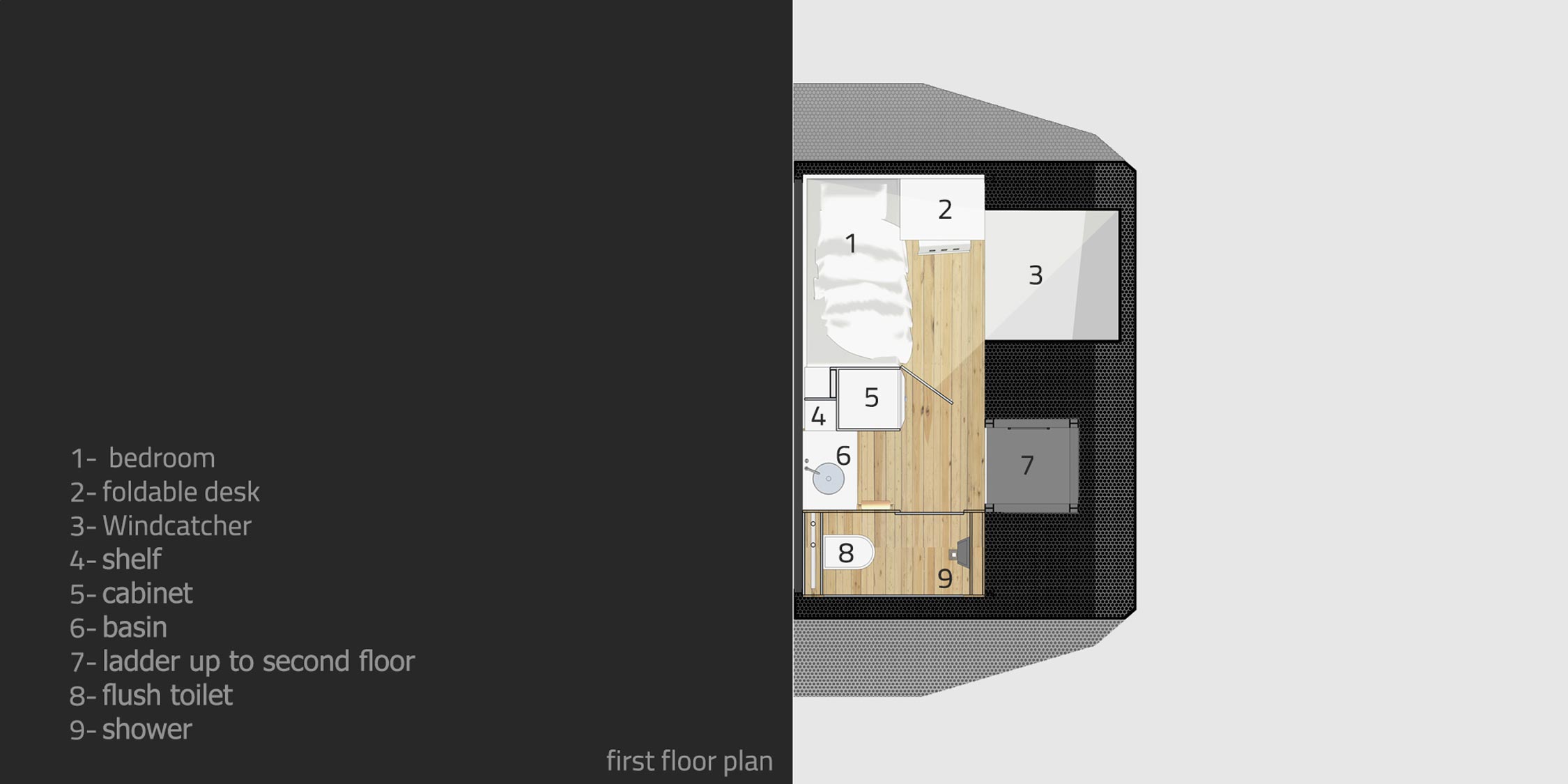
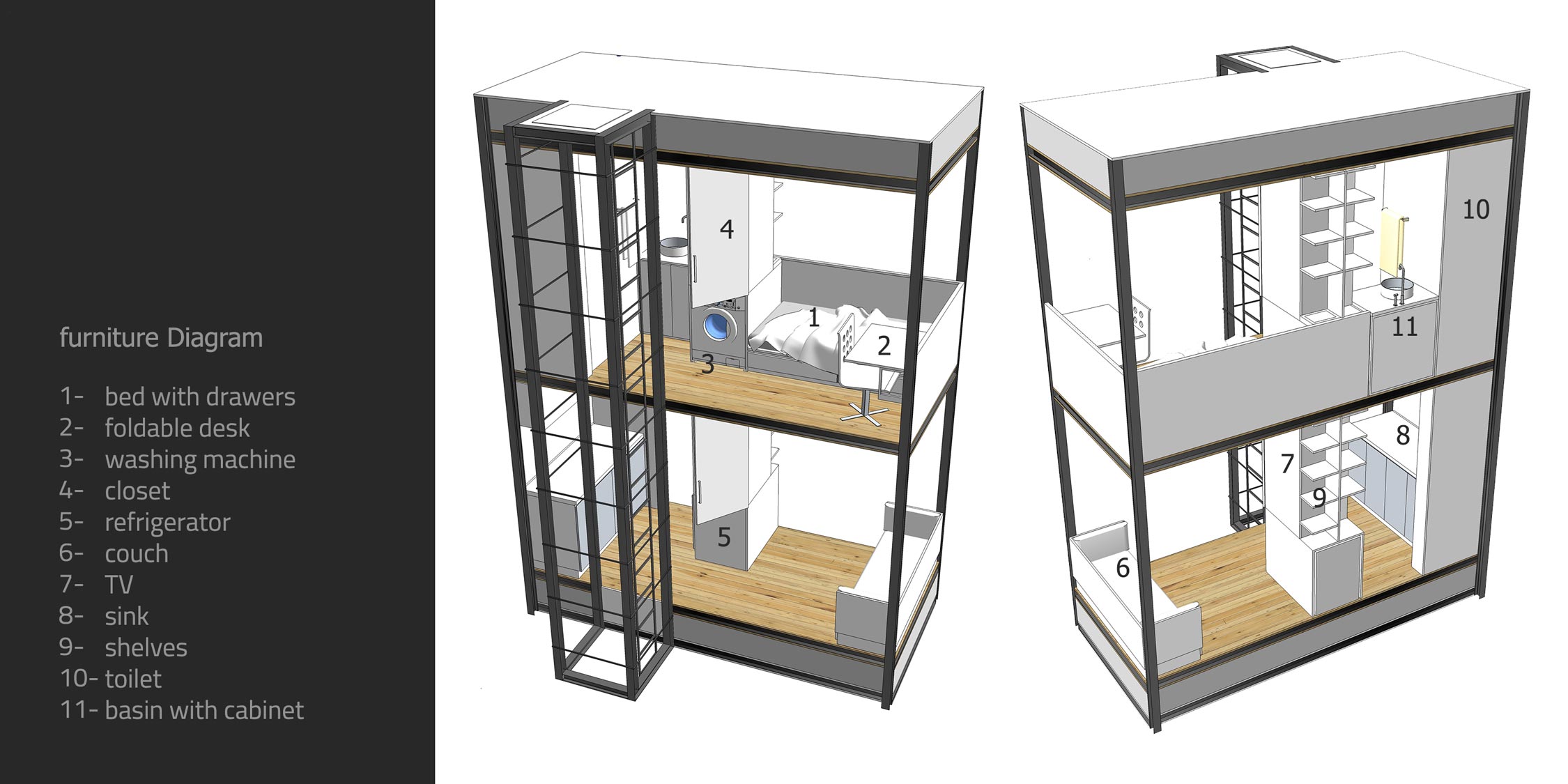
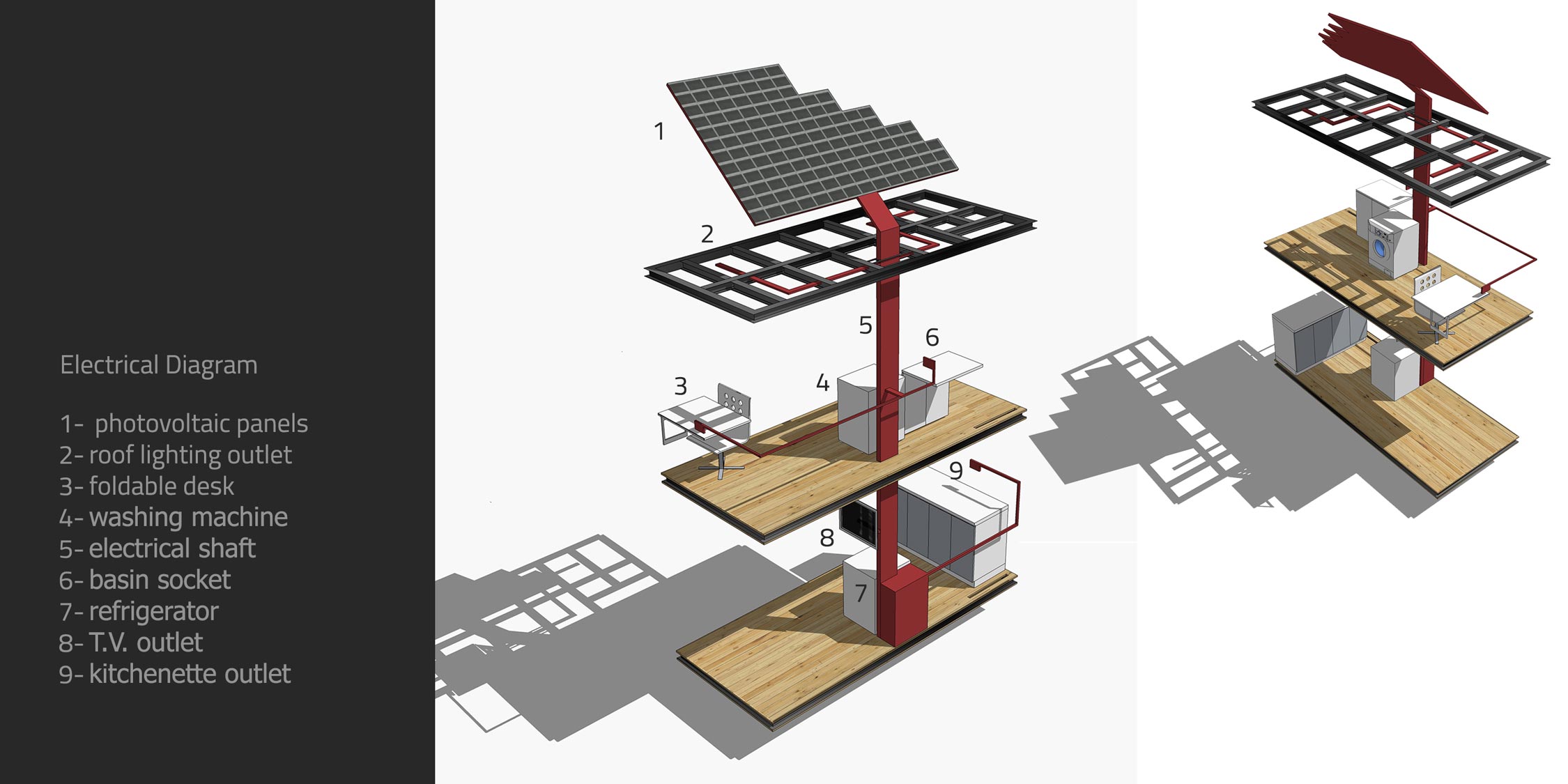
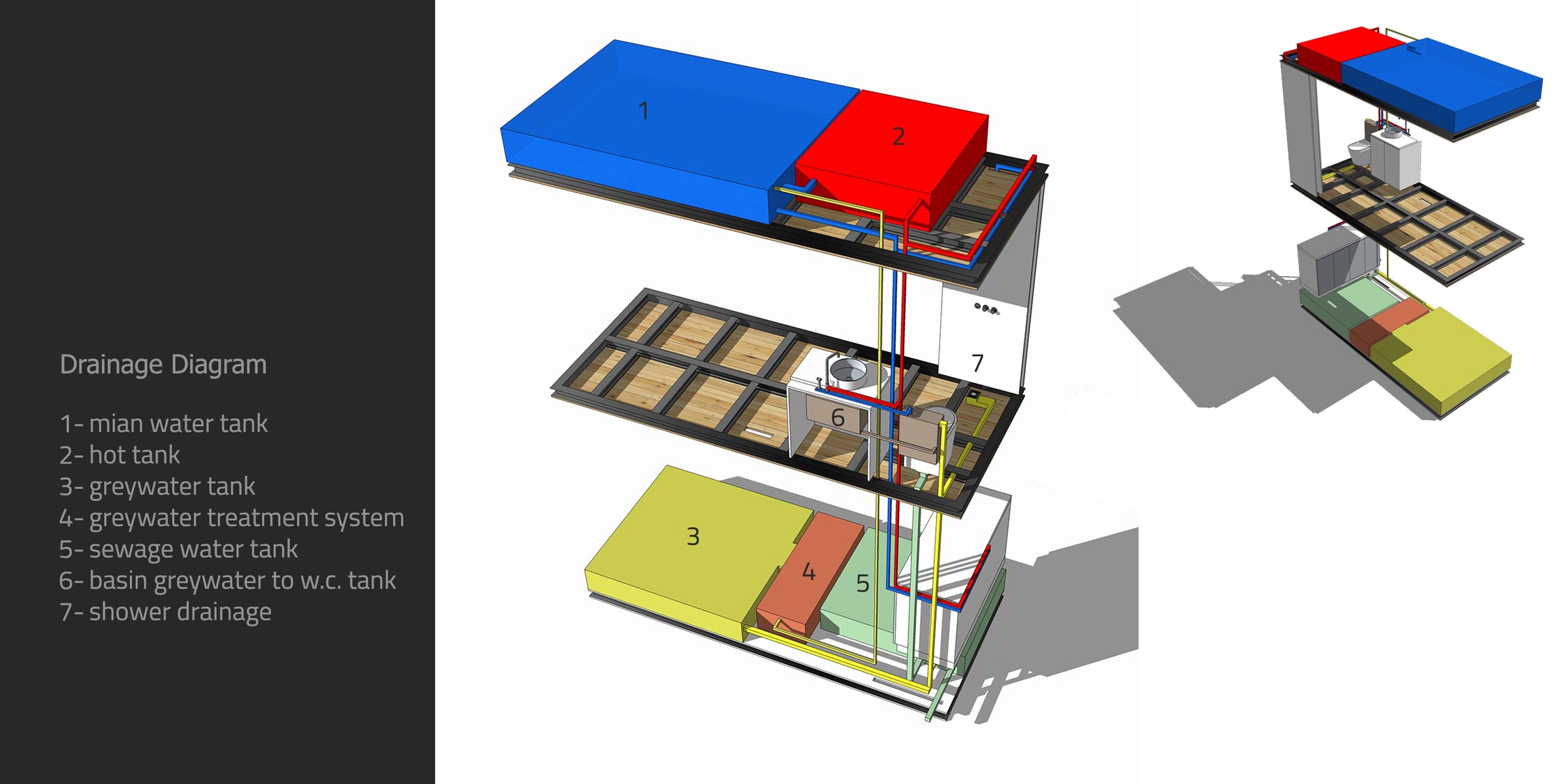
The Swallow Nest comprises two levels, each with an area of 7 square meters and is adorned with perforated steel panels to give it a contemporary look. The issue of renewable energy is also addressed in the Swallow Nest as it is equipped with solar panels installed on the roof and three other sides of the unit to generate power. Additionally, its sloped roof is designed to collect rainwater that is stored for future use. The unit also has a water purification system attached to its base to provide clean water.
The Swallow Nest is designed to be a sustainable housing unit in several ways. First, the use of renewable energy is a major feature of the design. The unit is equipped with solar panels that generate power, reducing the reliance on traditional energy sources. Additionally, the unit’s sloped roof collects rainwater that is stored for later use, reducing the need for additional water sources.
The Swallow Nest’s use of parasitic architecture is also a sustainable practice. Rather than building from scratch, the unit forms a relationship with a host building, using excess resources from the host to complete itself. This reduces the environmental impact of constructing a new building and utilizes existing resources.
The unit’s compact size is also a sustainable feature, as it requires less energy and resources to build and maintain than a larger dwelling. The use of perforated steel panels for the exterior not only gives it a modern look but also allows for natural light to enter the unit, reducing the need for artificial lighting.
Finally, the water purification system attached to the base of the unit ensures that clean water is always available, reducing the need for plastic water bottles and the waste that comes with them. Overall, the Swallow Nest’s design incorporates several sustainable practices, making it an environmentally conscious choice for adventurers and camper
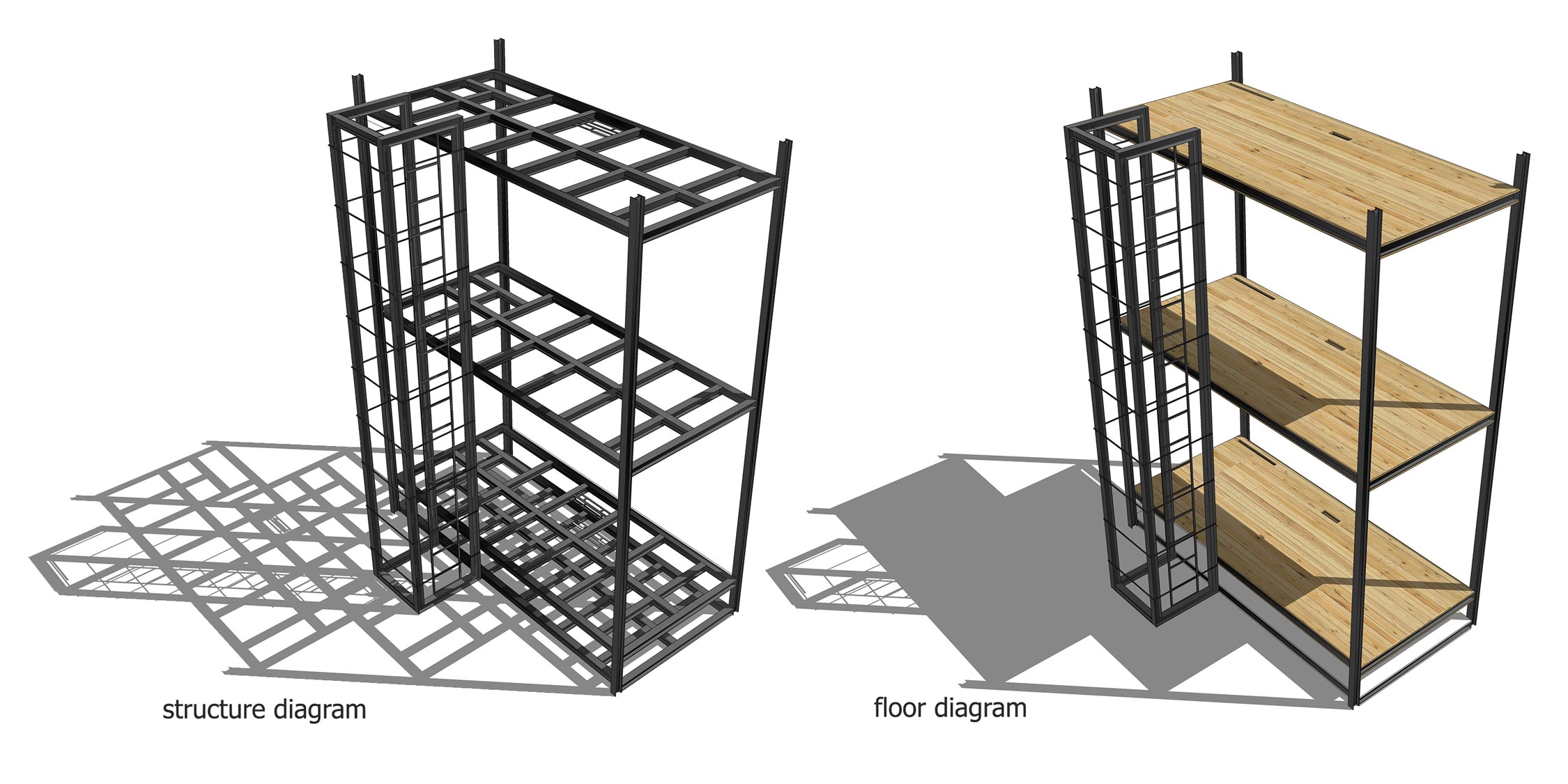
The Swallow Nest features a steel frame structure designed for durability and stability, with a network of columns and beams ensuring even load distribution. A vertical ladder is integrated into the design, allowing access between floors without occupying much space. The flooring consists of wooden panels, adding warmth to the interior, while perforated metal panels on the façade enhance ventilation and allow natural light, reducing reliance on artificial lighting. The unit is divided into two levels, each serving a distinct function—the upper floor is dedicated to sleeping and working, while the lower level accommodates seating and food preparation. Smart furniture solutions, such as a bed with built-in storage drawers, a foldable desk, and shelving units, optimize space efficiency and organization. The Swallow Nest’s compact design, reliance on renewable energy, and sustainable materials make it an ideal housing solution for adventurers, campers, and individuals seeking efficient living spaces in dense urban environments.